Introduction to Binomial Expansion
Binomial expansion is one of the cornerstones of algebra — a method that lets us expand expressions like (a+b)n(a + b)^n(a+b)n into a sum of multiple terms. Sounds fancy, right? But it’s actually a powerful tool used not just in school math but in physics, statistics, and even finance.
The concept dates back to ancient times but was popularized by Sir Isaac Newton, who extended it to include fractional and negative powers.
Table of Contents
What is a Binomial Expression?
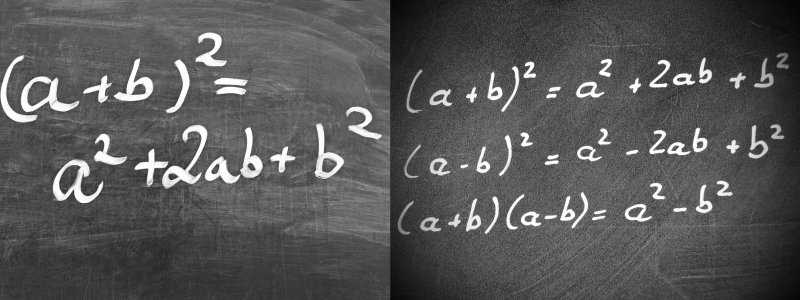
A binomial is a simple algebraic expression that contains exactly two terms, connected by either a plus (+) or minus (–) sign.
For example:
- a+ba + ba+b
- x−yx – yx−y
- 3p+4q3p + 4q3p+4q
A polynomial, on the other hand, can have many terms. So, a binomial is just a small, specific type of polynomial.
Pascal’s Triangle and Binomial Coefficients
Pascal’s Triangle is a simple way to find the coefficients in binomial expansions. Each number is the sum of the two directly above it.
Example:
1
1 1
1 2 1
1 3 3 1
1 4 6 4 1
These rows give the coefficients for (a+b)n(a + b)^n(a+b)n.
Examples Using Pascal’s Triangle
- (a+b)2=1a2+2ab+1b2(a + b)^2 = 1a^2 + 2ab + 1b^2(a+b)2=1a2+2ab+1b2
- (a+b)3=1a3+3a2b+3ab2+1b3(a + b)^3 = 1a^3 + 3a^2b + 3ab^2 + 1b^3(a+b)3=1a3+3a2b+3ab2+1b3
- (a+b)4=1a4+4a3b+6a2b2+4ab3+1b4(a + b)^4 = 1a^4 + 4a^3b + 6a^2b^2 + 4ab^3 + 1b^4(a+b)4=1a4+4a3b+6a2b2+4ab3+1b4
Applications of Binomial Expansion
In Calculus and Algebra
It makes complicated multiplications in algebra easier to understand. It aids in determining the integrals and derivatives of formulas employing powers in calculus.
In Statistics and Probability
The Binomial Probability Distribution, which models the number of successes in a series of independent experiments, is based on binomial expansion.
In Physics and Computer Science
It is employed in algorithms, polynomial approximations, and even the resolution of motion and energy-related physical equations.
Binomial Expansion in Real Life
Have you ever investigated how engineers create bridges or how computers forecast
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
Typical Errors and How to Prevent Them
Using binomial coefficients, such as 1, 2, 3, 6, etc., is always preferable to forgetting them.
Sign errors: When extending (a−b)n, be cautious with negative signs.
Power misalignment: Ensure that the powers of b rise and those of a fall.
Simplifying Binomial Expressions
Example: (2x+3)3=8×3+36×2+54x+27(2x + 3)^3 = 8x^3 + 36x^2 + 54x + 27(2x+3)3=8×3+36×2+54x+27
Step-by-step:
- Use coefficients 1, 3, 3, 1.
- Multiply each term by powers of 2x and 3.
- Combine terms neatly.
Using the Binomial Theorem for Approximation
For small values of xxx, the expansion: (1+x)n≈1+nx+n(n−1)x22!+…(1 + x)^n \approx 1 + nx + \frac{n(n-1)x^2}{2!} + …(1+x)n≈1+nx+2!n(n−1)x2+…
is useful in estimating roots or interest rates without calculators — a trick scientists and engineers often use.
Advanced Concepts
Negative and Fractional Exponents
Newton extended the theorem for any real number nnn:
(1+x)n=1+nx+2!n(n−1)x2+…
This creates an infinite series, which is used in advanced calculus.
Practice Problems
- Expand (x+2)4(x + 2)^4(x+2)4.
- Expand (a−b)5(a – b)^5(a−b)5.
- Use binomial theorem to find the 4th term in (2x+3)6(2x + 3)^6(2x+3)6.
- Approximate (1.02)5(1.02)^5(1.02)5 using the first three terms.
Tip: Always remember the formula (nk)=n!k!(n−k)!\binom{n}{k} = \frac{n!}{k!(n-k)!}(kn)=k!(n−k)!n!.
Conclusion
Binomial expansion is more than just an algebraic trick — it’s a mathematical language that connects algebra, statistics, and even physics. Once you master it, you’ll start seeing its presence in everything from coding to financial models.
FAQs
What is the easiest way to learn binomial expansion?
Before moving on to the formula, begin by discussing Pascal’s Triangle and small powers.
Why is Pascal’s triangle important?
For every term in the growth, it provides you with the values immediately.
Can binomial expansion work with negative powers?
Yes, applying Newton’s Binomial Theorem in its generalized form.
Where do we use binomial expansion in real life?
In probability, physics, computer algorithms, and financial calculations.
How to remember binomial coefficients easily?
Use Pascal’s Triangle — it’s a simple visual memory tool!

